In the fascinating world of animal behavior, communication goes far beyond the typical sounds animals make. While vocalizations are certainly important in some species, many animals communicate through a much subtler medium: body language. From the wagging of a dog’s tail to the flick of a cat’s ears, animals use their bodies to convey a rich array of emotions, intentions, and messages. Understanding trough Animal Body Language Quiz, these non-verbal signals is key to improving our interactions with animals, whether they are pets, wildlife, or farm animals.
This comprehensive guide on animal body language delves into the significance of various body signals and provides an Animal Body Language Quiz at the end to test your knowledge. Whether you’re an experienced pet owner or just someone curious about the silent language animals use to communicate, this article will provide valuable insights into the world of animal behavior.
Key Takeaways
- Posture, tail movements, and ear positions are the primary ways animals communicate their feelings.
- Understanding species-specific behavior is essential to interpreting animal body language accurately.
- Animals use facial expressions and eye contact to further emphasize their emotions, from aggression to affection.
- Tail wagging, ear flattening, and eye dilation are powerful signals that provide immediate insight into an animal’s emotional state.
- Being able to interpret these signals helps to improve safety, build trust with pets, and better understand wildlife behavior.
The Importance of Understanding Animal Body Language
Animals have evolved over millennia to communicate with each other and with humans through body language. For pet owners, understanding animal body language can enhance the relationship with their pets, ensuring that their emotional needs are met and preventing potential misunderstandings. In wildlife contexts, understanding the body language of animals can also help humans avoid dangerous situations and interpret wildlife behavior from a safe distance.
Being able to interpret these signals effectively is not just about understanding animals; it’s about building trust and a deeper connection with them. By recognizing the meanings behind different movements and positions, you can ensure that animals feel safe and understood, thereby improving their well-being and your interactions with them.
Decoding Animal Body Language
Animal body language encompasses various physical cues such as posture, facial expressions, tail movements, eye contact, and ear positions. These signals can vary across species but often share common elements, making it possible for humans to understand them with some practice. Below is a detailed explanation of the key elements of animal body language, starting with the basics.
1. Posture: The Foundation of Communication
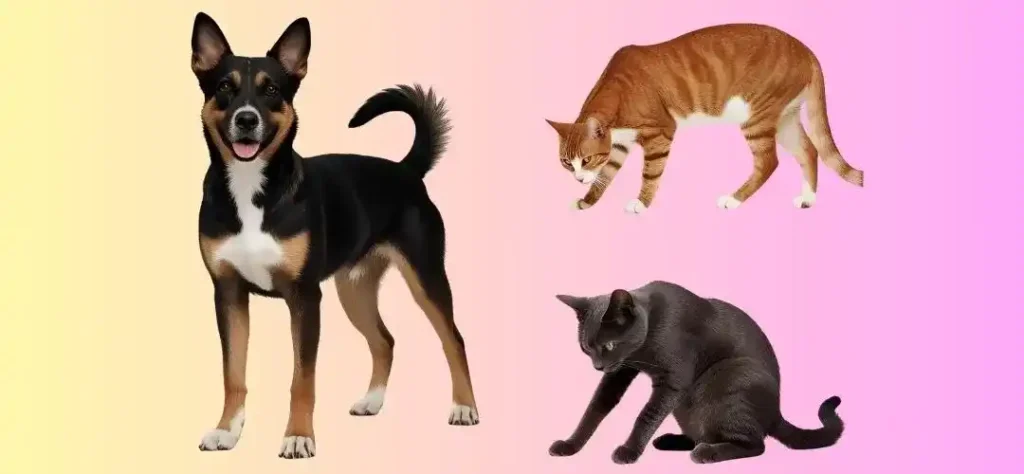
The way an animal positions its body plays a huge role in conveying its feelings. From a dog’s confident stance to a cat’s defensive crouch, posture is a clear and immediate signal of an animal’s emotional state.
- Relaxed Posture: When an animal is calm and comfortable, it will adopt a neutral, relaxed posture. In dogs, this might involve standing with their body slightly angled, their tail relaxed, and their ears facing forward. Cats may lie down in a stretched position with their eyes half-closed, indicating that they are at ease.
- Aggressive Posture: An aggressive animal will often have a rigid or tense posture. For dogs, this could mean standing with the tail straight and ears stiffly pointing forward. Cats may arch their backs, puffing up their fur to appear larger and more intimidating.
- Defensive Posture: Animals feeling threatened or scared will shrink their body size to appear less vulnerable. For example, a dog with its body lowered and tail between its legs is likely experiencing fear. Cats often crouch and try to make themselves appear smaller when frightened.
2. Tail Movements: Emotions on Display

The tail is one of the most expressive parts of an animal’s body. A dog wagging its tail is often considered a sign of happiness, but the context and speed of the wagging can alter its meaning.
- Fast Wagging Tail (Dogs): A fast wagging tail indicates excitement, joy, or enthusiasm. However, if the wagging is accompanied by stiff body movements, it could be a sign of agitation or unease.
- Tucked Tail: Dogs tuck their tail between their legs as a sign of fear, anxiety, or submission. It’s a sign that the dog is feeling threatened or intimidated.
- Tail Flicking (Cats): A rapidly flicking tail in a cat signals annoyance or agitation. It’s a clear sign that the cat is displeased or frustrated. However, a gently waving tail indicates curiosity or interest.
3. Ear Position: Listening with the Body
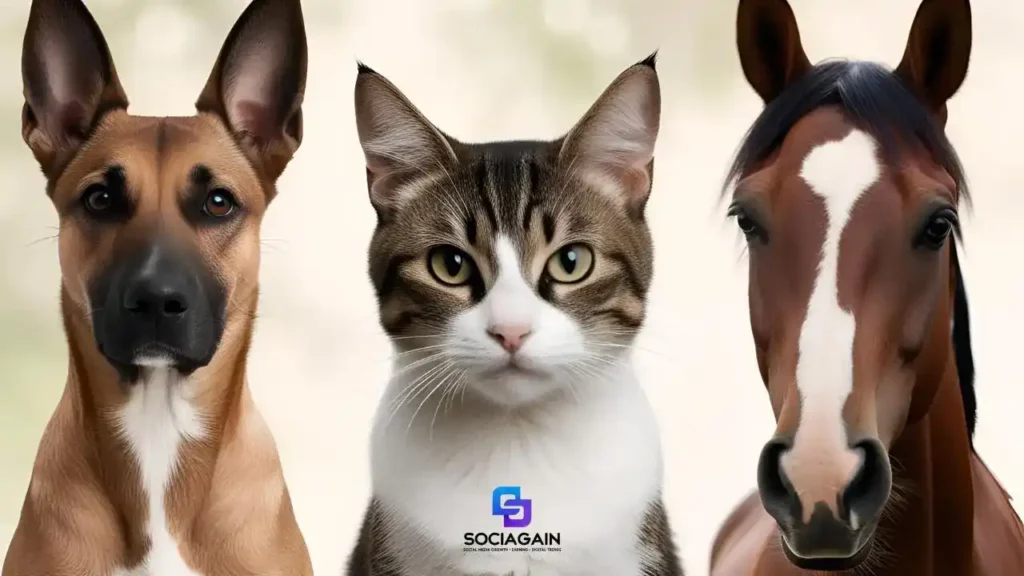

An animal’s ear position is another reliable indicator of its emotional state. Ears can reflect everything from curiosity and attentiveness to aggression and fear.
- Forward Ears: When an animal has its ears pointed forward, it is usually engaged, interested, or alert. For dogs, forward ears often indicate curiosity or excitement about something in their environment.
- Flat Ears: Cats and dogs often flatten their ears against their heads when they feel threatened or defensive. This is an attempt to protect their ears and communicate that they are not happy with the current situation.
- Sideways Ears: When a dog or cat positions its ears sideways, it often indicates confusion or stress. The animal is unsure about its surroundings or how to react to something.
4. Eye Contact: A Window into the Soul
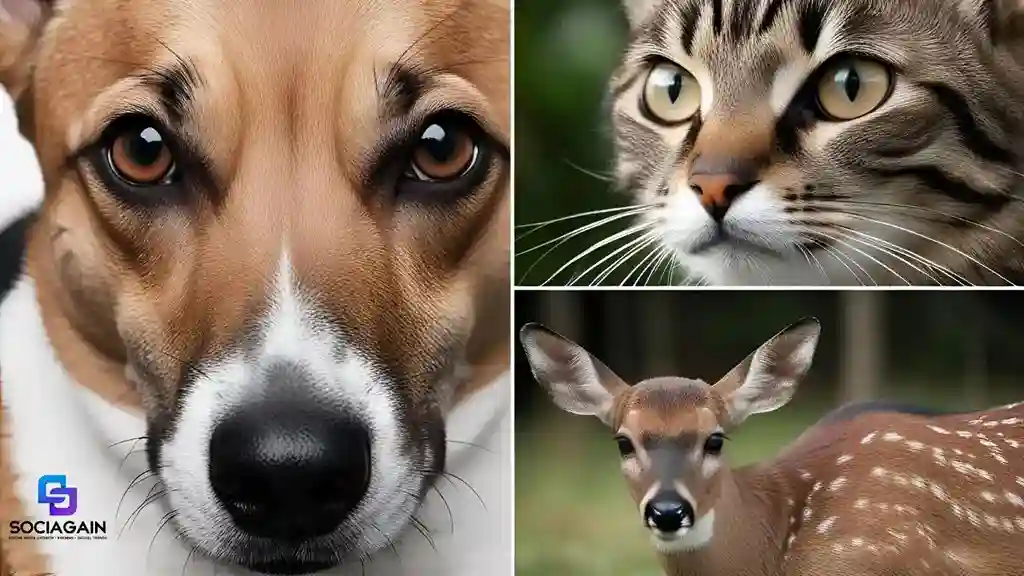

Eye contact can be both a friendly gesture and a challenge, depending on the species. Animals use their eyes to convey trust, curiosity, fear, or aggression.
- Direct Eye Contact: In many species, including dogs, prolonged eye contact is often perceived as a threat. However, some dogs and humans may use eye contact as a form of affection or to bond.
- Soft Eyes: Soft, relaxed eyes in animals such as cats and dogs indicate contentment. A cat slowly blinking at you is a sign of affection, while a relaxed dog may exhibit soft eyes as it lounges or rests.
- Dilated Pupils: Dilated pupils can indicate heightened excitement or fear. For instance, a cat with dilated pupils may be in a state of alertness or fear, while a dog’s dilated pupils can indicate anxiety or arousal.
5. Facial Expressions: The Subtle Art of Expression
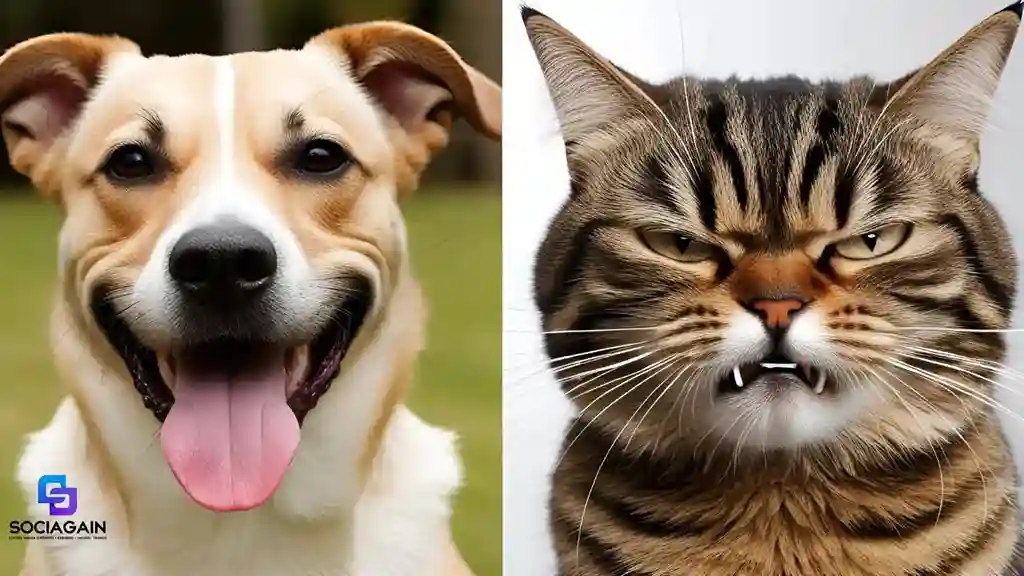

Animals don’t have the full range of facial expressions that humans do, but they can still communicate a lot through their faces. Dogs and cats, in particular, use facial muscles to express various emotions.
- Dogs: A dog with a relaxed mouth, slightly open, and soft eyes is generally calm. When a dog pulls its lips back to show teeth, it can be a sign of aggression, fear, or a warning to back off.
- Cats: A cat’s facial expression is often subtle. A relaxed, neutral face means the cat is content, while a furrowed brow or wrinkled nose may indicate irritation or displeasure.
6. Vocalizations: Adding Sound to the Message
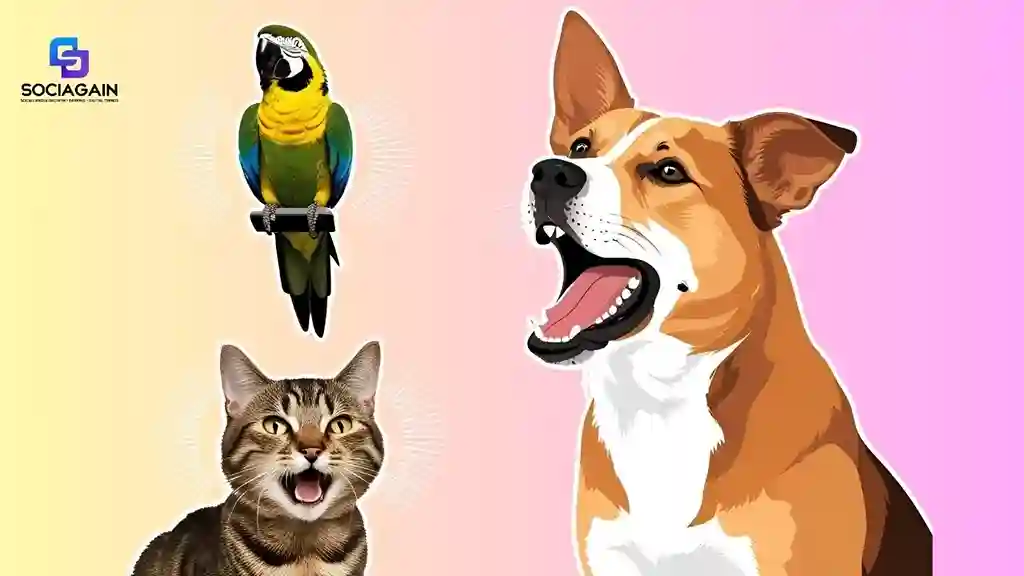

In addition to body language, many animals communicate with sounds. From a dog’s bark to a bird’s song, vocalizations are often used to reinforce or emphasize non-verbal cues.
- Dogs: Barking can range from excitement to warning, while whining or growling can signal discomfort, frustration, or aggression.
- Cats: Meowing, purring, and hissing are all distinct vocalizations that express a range of emotions. Meowing is often a request for attention, while hissing is an aggressive or defensive vocalization.
Species-Specific Animal Body Language

Each species has its own unique ways of using body language. Let’s explore how some specific animals communicate with their bodies.
1. Dogs: Man’s Best Friend
Dogs have been companions to humans for thousands of years, and their body language has evolved to communicate with us. By paying attention to their tails, ears, and posture, we can better understand their moods.
- Happy Dog: A dog that is wagging its tail vigorously, jumping up, and has a relaxed posture is likely feeling joyful.
- Aggressive Dog: When a dog stiffens its body, raises its hackles, and growls, it’s signaling that it feels threatened and may become aggressive if provoked.
- Fearful Dog: A dog that tucks its tail, crouches low, or backs away may be fearful of a situation or person.
2. Cats: Independent and Subtle
Cats are more subtle than dogs in their body language, but they still communicate effectively through their tails, ears, and facial expressions.
- Content Cat: A purring cat with its body relaxed and eyes half-closed is expressing contentment and trust.
- Aggressive Cat: An aggressive cat will arch its back, puff up its fur, and may show its teeth as a warning sign.
- Anxious Cat: A fearful or anxious cat may crouch, with its tail tucked and eyes wide open. It might also hiss or swat if it feels threatened.
3. Birds: Colorful Communicators
Birds, particularly parrots, use a combination of body language, feathers, and vocalizations to express their emotions.
- Friendly Bird: A bird that is singing, hopping, and preening is likely in a positive, comfortable mood.
- Aggressive Bird: When a bird fluffs its feathers, opens its beak, and hisses, it is signaling that it feels threatened or aggressive.
- Fearful Bird: Birds may freeze or attempt to fly away when they feel scared. Their eyes may also widen, and their posture becomes rigid.
- you may also be interested in Bat Stuffed Animal: A Unique and Adorable Plush Toy
4. Horses: Majestic Body Language
Horses communicate through their ears, tail, and overall posture. Understanding these signals can make handling them safer and more effective.
- Calm Horse: A relaxed horse will stand with its ears slightly forward, its body loose, and its tail low.
- Anxious Horse: A horse that is stomping, has its ears back, and is pacing may be feeling nervous or uneasy.
- Aggressive Horse: Horses can display aggression by flattening their ears, showing their teeth, or kicking.
Animal Body Language Quiz
Now that you have a better understanding of animal body language, let’s see how much you’ve learned. Take the Animal Body Language Quiz below and test your knowledge!
1. What does it mean when a dog stands with its tail high and ears forward?
- A) Relaxed
- B) Aggressive or dominant
- C) Fearful
- D) Submissive
2. What does a cat’s slow blink usually indicate?
- A) Aggression
- B) Happiness and trust
- C) Fear
- D) Curiosity
3. What does a bird puffing up its feathers and hissing likely mean?
- A) It is scared or aggressive
- B) It wants to be left alone
- C) It is curious
- D) It is playing
4. What does a horse with its ears flat against its head typically indicate?
- A) Fear or aggression
- B) Calmness
- C) Curiosity
- D) Happiness
5. When a dog tucks its tail between its legs, what is it feeling?
- A) Confidence
- B) Excitement
- C) Fear or submission
- D) Playfulness

FAQs (Animal Body Language Quiz)
1. Why is animal body language so important?
Understanding animal body language is crucial for building trust and enhancing communication between humans and animals. It helps us understand an animal’s emotional state, which is particularly important for ensuring safety and preventing misunderstandings in various environments.
2. What are the most common signs of a scared animal?
Common signs of fear in animals include tucked tails (dogs), crouched bodies (cats), ears flattened against the head, wide eyes, and defensive postures. Animals may also freeze, attempt to hide, or attempt to escape from perceived threats.
3. How can I tell if my dog is happy or stressed?
A happy dog typically exhibits relaxed posture, wagging its tail, and has soft eyes. In contrast, a stressed dog may have a stiff posture, wag its tail slowly or erratically, and avoid eye contact. A stressed dog may also exhibit other signs such as panting or drooling excessively.
you may also like to read Is Nylabone Safe for Dogs? Guide for Pet Owners
4. Can animals communicate with each other through body language?
Yes, animals of the same species frequently use body language to communicate. For example, dogs often use body posture and facial expressions to communicate with other dogs, while birds may use specific movements and displays to communicate their emotions to fellow birds.
Conclusion
Understanding animal body language is not only a fascinating area of study but also an essential skill for anyone interacting with animals. Whether you’re a pet owner, a wildlife enthusiast, or someone who works closely with animals, the ability to interpret their body language can significantly improve the quality of your interactions. By recognizing the subtle signals animals send through their posture, ears, tail movements, eye contact, and facial expressions, you can create a deeper, more empathetic connection with the creatures around you.
As we’ve discussed in this article, animals communicate much more than we may initially think. Every tail wag, ear flick, or posture shift has meaning. By learning to understand these cues, we ensure a safer environment for both humans and animals. It also enriches the relationships we share with our pets and provides a new perspective on how we view and understand wildlife.
Furthermore, as we’ve seen in the Animal Body Language Quiz, these signals are not limited to pets like dogs and cats but extend across species. Each animal, whether a bird, horse, or wild creature, has developed its own unique set of body language cues to communicate with others of its kind—and with us.
So, the next time you’re interacting with an animal, take a moment to observe its body language. Whether it’s a dog wagging its tail, a cat slowly blinking, or a bird fluffing its feathers, remember that these actions speak volumes. The more you learn to read these signals, the better equipped you’ll be to understand your animal companions and engage with them in a more meaningful way.
If you’re interested in continuing your exploration of animal behavior, keep observing and engaging with animals, and maybe even try conducting your own animal body language quiz with your friends or family! The more we learn about how animals communicate, the better we can ensure they feel heard, safe, and respected.
Explore more on SociaGain




